Rivers Of India







Rivers Of India
Rivers Of India
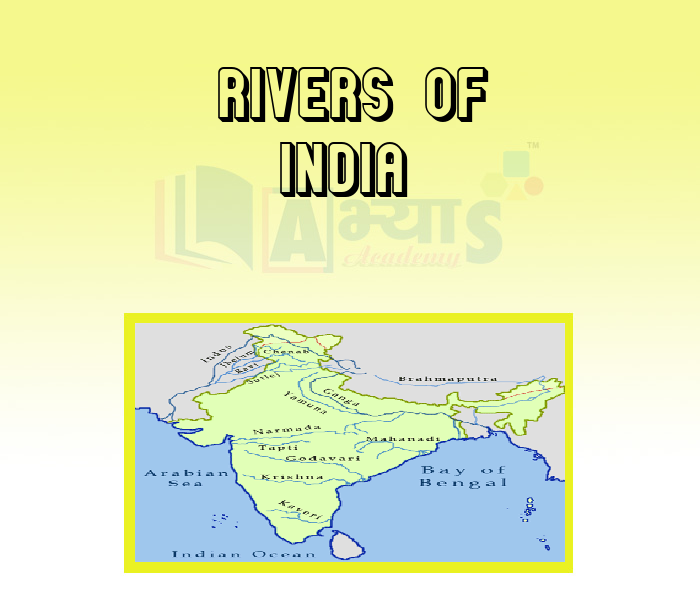
The rivers of India may be classified as follow:
(a) Himalayan rivers.
(b) The Deccan rivers,
(c) The Coastal rivers and
(d) The rivers of the Inland Drainage Basin.
The Himalayan rivers are generally snow fed and have, therefore, continuous flow throughout the year. The Deccan rivers are generally rain fed and, therefore, fluctuate very much in volume. The coastal streams, especially of the west coast, are short in length and have limited catchment areas. The streams in the Inland Drainage Basin of Western Rajasthan are few, and far between.
The Ganga basin, which receives waters from an area of about one-quarter of the total area of India, is largest. Its boundaries are defined the Himalayas in the north and the Vindhya mountains in the south. The Ganga has Bhagirathi and the Alaknanda, the former rising from the Gangotri glacier of Gaumukh and the latter from a glacial spout of the Alkapur Glacier. A number of Himalayan Rivers including the Yamuna, Ghaghra, Gomti, Gandak and Kosi join Ganga. the Himalayas in the north and the Vindhya mountains in the south.
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
About Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice
